Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics
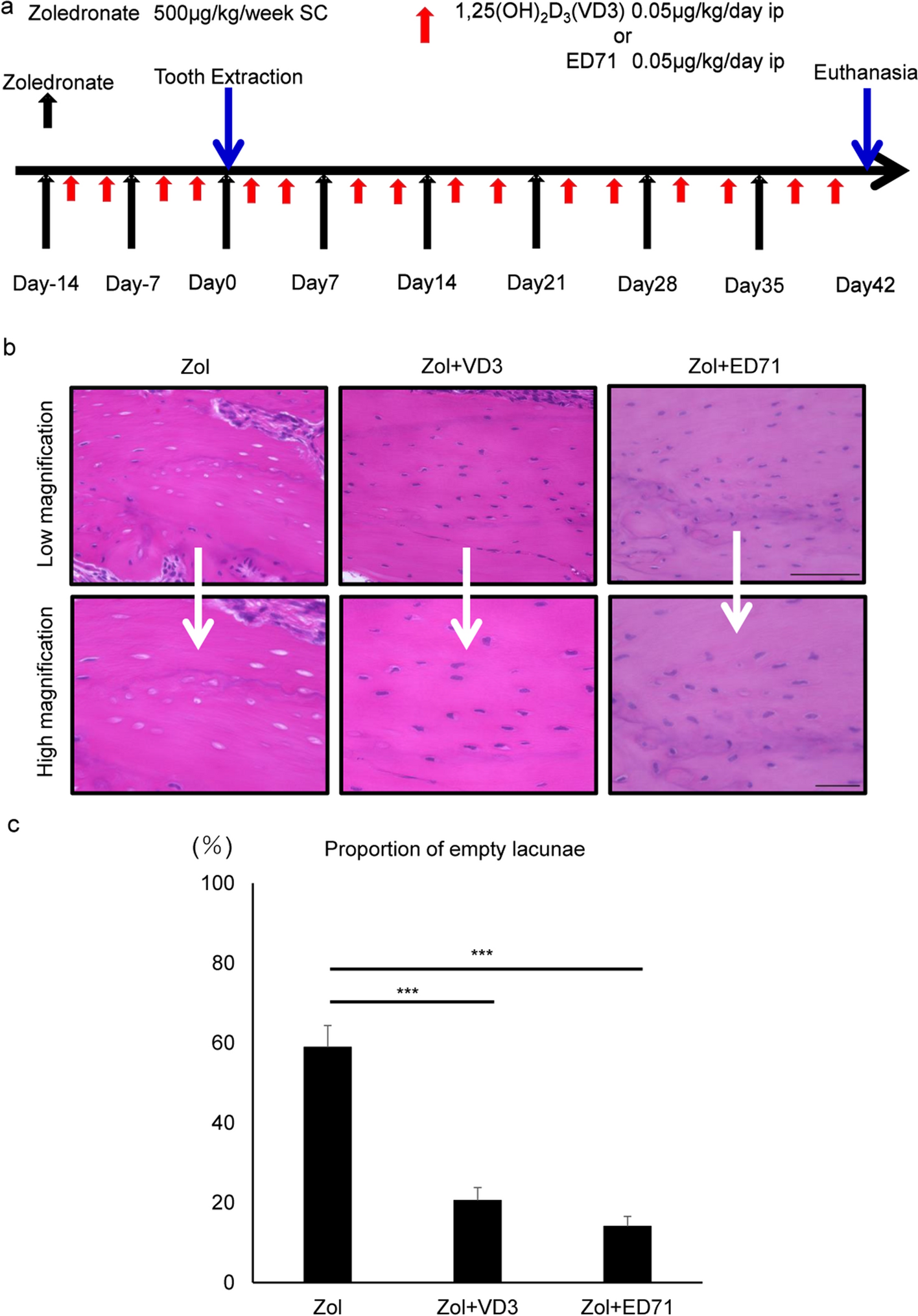
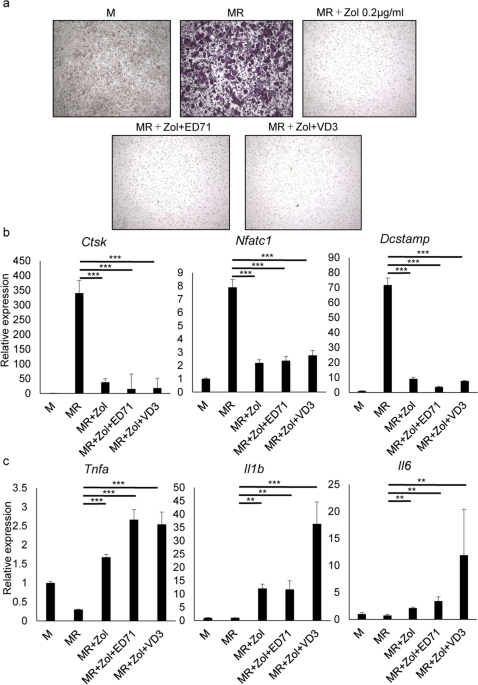
Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics

Bisphosphonates, Old Friends of Bones and New Trends in Clinics
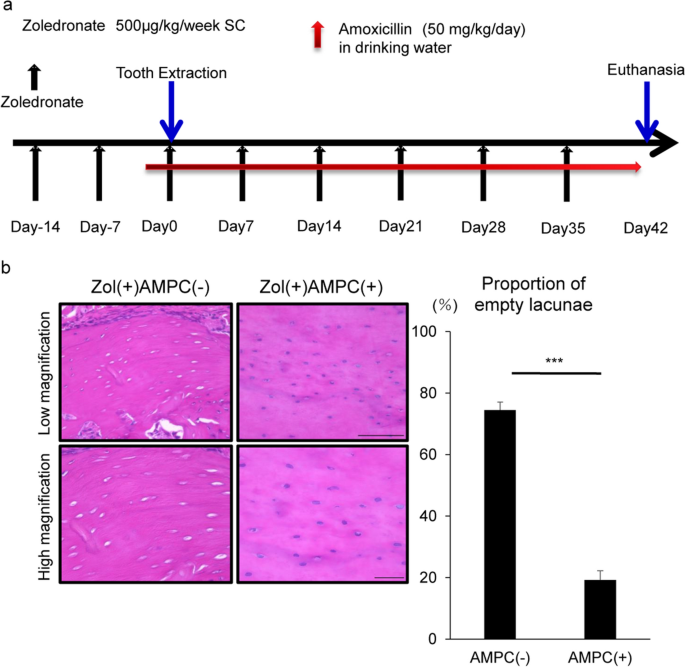
Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics
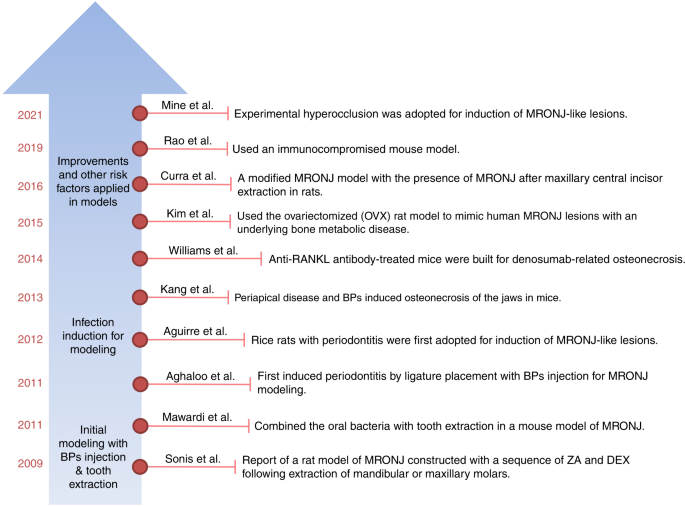
Establishment and assessment of rodent models of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ)
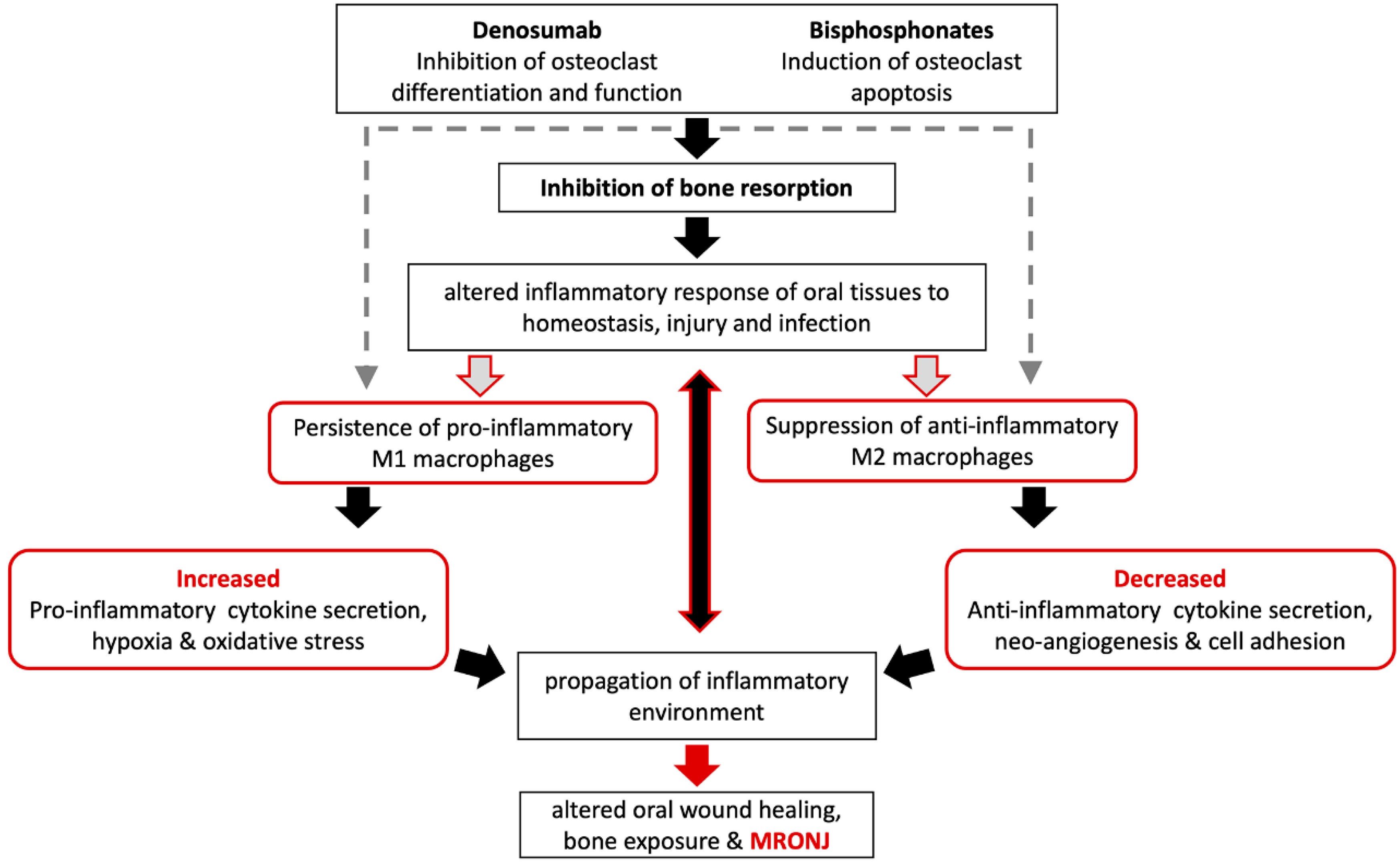
Cancers, Free Full-Text

Tooth extraction in mice administered zoledronate increases inflammatory cytokine levels and promotes osteonecrosis of the jaw

Pathophysiology of Medication‐Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw—A Minireview - Tetradis - 2023 - JBMR Plus - Wiley Online Library

IJMS, Free Full-Text
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws after tooth extraction in senescent female mice treated with zoledronic acid: Microtomographic, histological and immunohistochemical characterization

PDF) Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics








